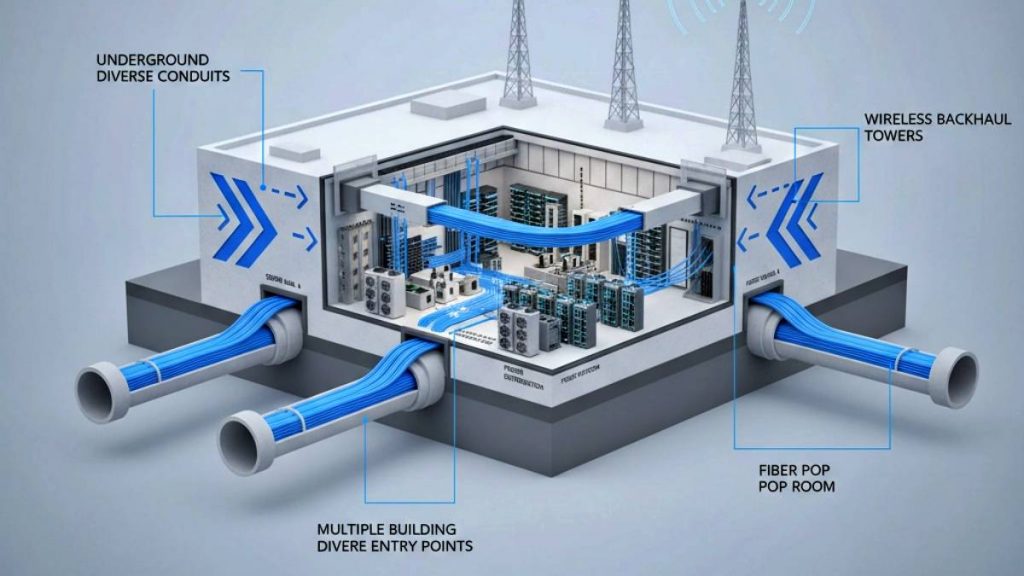
Business IT functions can be deployed to a data center for the scalability, reliability, and security that comes with professional infrastructure. A critical component of any colocation setup is the network connectivity between your business, the data center, and the Internet. Your choice of network connectivity should provide fast, secure, and consistent access. Let’s examine the primary connectivity options, weighing the pros and cons of each, to help you make an informed decision.
Dedicated Internet Access (DIA)
Dedicated Internet Access (DIA) provides a dedicated, high-speed internet connection, where the total bandwidth is reserved exclusively for your use. This option is particularly popular among businesses that require consistent and high-performance internet service to support cloud applications, remote users, and large-scale data transfers.
Pros:
- Guaranteed Performance: DIA typically offers minimum speed guarantees for upload and download, ensuring optimal performance for bandwidth-intensive operations.
- Service-Level Agreements (SLAs): Most DIA providers offer strong SLAs that guarantee high uptime and low latency, giving businesses the reliability they need.
- Security: Because DIA connections are private, they inherently offer greater security than shared internet services.
Cons:
- Cost: The dedicated nature of DIA makes it more expensive than shared alternatives.
- Lack of Redundancy: A single DIA connection provides no inherent redundancy. To achieve a failover setup, businesses must invest in multiple DIAs from different providers and manage the necessary hardware for path diversity, which adds to the complexity and cost.
Best Fit: DIA is ideal for businesses heavily reliant on cloud-based services or those that need consistent, high-speed access for demanding applications.
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS)
MPLS is a private networking technology that allows data to be routed based on predefined labels rather than traditional IP addresses. It is known for providing highly efficient and low-latency connectivity. It is preferred by businesses with multiple office locations or those requiring a reliable connection between offices and data centers.
Pros:
- Low Latency and High Reliability: MPLS networks are designed for efficient data transport, making them suitable for real-time applications like VoIP and video conferencing.
- Enhanced Security: Since MPLS is a private network, it doesn’t traverse the public Internet, offering an added layer of protection.
- Scalability: MPLS networks can easily accommodate the expansion of your business, whether it’s adding more locations or increasing bandwidth.
Cons:
- High Cost: MPLS is one of the more expensive connectivity options, particularly for businesses with extensive geographical coverage.
- Vendor Lock-In: Many MPLS contracts are long-term and can limit flexibility, making it difficult to switch providers if your needs change.
Best Fit: MPLS is well-suited for enterprises that require consistent, low-latency connections across multiple locations or have high-security data transport requirements.
Point-to-Point (PTP) Connections
A Point-to-Point (PTP) connection provides a dedicated link between your business location and the data center, without passing through the public Internet. This type of connection is highly secure and efficient, as it establishes a direct path for data transmission.
Pros:
- High Performance: With a direct connection, you get fast and consistent data transfer speeds with minimal latency, making PTP suitable for mission-critical applications.
- Exceptional Security: Since the connection does not use the public Internet, the risk of data interception is greatly reduced, providing peace of mind for businesses with strict compliance or data protection needs.
- No Congestion: The dedicated nature of a PTP link ensures that network congestion will not affect your connection quality.
Cons:
- WAN Access Limitations: If your business requires access to the public Internet, you must route all traffic through the PTP connection’s remote side or invest in a secondary DIA connection at the data center. This adds to the complexity and cost and can increase latency.
- Cost and Infrastructure: PTP connections can be expensive to establish and maintain, particularly over long distances, and may require significant network infrastructure investment.
Best Fit: PTP is a strong choice for businesses needing a high-security, high-performance link between their office and data center, especially for applications sensitive to latency or packet loss.
Data Center House Blend
Many data centers offer a “house blend” service, which aggregates connectivity from multiple ISPs into a single, managed service. This option provides businesses a cost-effective way to gain redundant, high-speed internet access while minimizing administrative overhead.
Pros:
- Built-In Redundancy: With access to multiple ISPs, the risk of downtime is significantly reduced, as traffic can be rerouted in case of an issue with one provider.
- Simplified Management: You have one point of contact for network issues, making troubleshooting and administration easier.
- Cost-Effective: House blend services can be more affordable than setting up multiple individual connections and typically come with flexible bandwidth options.
Cons:
- Limited Control: Your choice of ISPs is restricted to what the data center offers, which may not always align with your preferences.
- Potential Congestion: Although redundancy is built in, shared infrastructure may experience some congestion during peak usage times.
Best Fit: A house blend is perfect for businesses looking for convenient, reliable internet access with built-in redundancy, without wanting to manage multiple service providers.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business
When evaluating your connectivity options, consider your business’s unique requirements:
- Performance Needs: If your applications are sensitive to latency or if you handle high data volumes, prioritize high-speed, low-latency solutions like PTP or MPLS.
- Budget Constraints: Balancing cost and performance is crucial. DIA and MPLS provide excellent service but at a premium. Evaluate whether a cost-effective house blend might meet your needs without breaking the bank.
- Security Requirements: If data protection is a priority, MPLS or PTP will provide the highest levels of security. However, adding security features to a DIA setup can also be effective.
- Redundancy: Consider how critical uptime is to your business. If redundancy is essential, you may need to invest in multiple DIA connections or rely on a house blend service.
Conclusion
Choosing the best connectivity solution for your data center colocation can significantly impact your business’s efficiency, security, and overall success. Carefully assess your operational needs, budget, and long-term growth plans to make an informed decision. At Datacate, our experts are here to guide you through this process and implement the connectivity solutions that best align with your goals. Contact us today to optimize your data center experience and ensure your business runs smoothly.